Zero Leak Projection
The Zero Leak Projection is based on the assumption that there is one 0.0 PSI leak in the cable. It uses cable pressure, flow rates and pneumatic resistance to indicate how far the zero leak is from the measurement point. Any smaller leak—a leak reducing cable pressure to a level greater than zero PSI—must be closer to the air source than the projected distance. If there are two or more leaks causing the flow increase, at least one of them must be within the ZLP boundary.In order to make a Zero Leak Projection, three pieces of information are required:
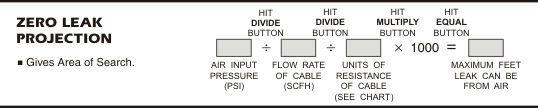
The Zero Leak Projection is based on the assumption that there is one 0.0 PSI leak in the cable. It uses cable pressure, flow rates and pneumatic resistance to indicate how far the zero leak is from the measurement point. Any smaller leak—a leak reducing cable pressure to a level greater than zero PSI—must be closer to the air source than the projected distance. If there are two or more leaks causing the flow increase, at least one of them must be within the ZLP boundary.In order to make a Zero Leak Projection, three pieces of information are required:
- Input pressure to the cable. Input pressure is determined primarily by using the C pressure gauge. Use the pressure testing valve associated with the air source and note the reading to the nearest one hundredth (0.01) of a PSI.
- Flow rate into the cable in SCFH. The flow rater or Flow Gauge can be used to determine cable flow rates. Depending on the location and/or type of device to be read, either a Flow Gauge or a portable or panel-mounted flow rater is used. Note: You can also calculate the flow rate, as explained in this section, and use the information in a ZLP.
- Pneumatic resistance of the cable per 1,000 feet. The unit resistance of the cable can be determined by using the pneumatic resistance tables listed in the previous section, "The Basics of Pressure." In explanations throughout this manual, references to pair numbers are abbreviated. On all pair designations of 100 pairs or more, the zeros are dropped. For example, A 900 pair, 22 gauge cable is designated as 9-22.
